NeQter Labs Initial Setup Guide
Backups
Making sure you have logs archived and ready to be restored in case of an issue occurring is a very integral part of becoming NIST Compliant, to access this section in your NeQter Client, go to Settings > Backups
Log types
There are two types of logs in the eyes of the Backups system.
- Visualized logs: Visualized logs are logs that are searchable and visualized in NeQter’s dashboards. Visualized logs are stored within NeQter’s indices and take much more space to store than archived logs.
- Archived logs: Archived logs are logs that have been brought out of NeQter and stored in a compressed format. Archives can live on NeQter’s internal storage or on an external file server. Because archives are compressed, they take much less space than visualized logs. Archived logs can be restored back into NeQter’s indices in order to be visualized again.
Backup services
Archival
The backup service runs every day at midnight. The backup service will begin by archiving all visualized logs that meet the user configured archive age.
NOTE: This operation cannot be interrupted once it begins. This process may take a long time.
Deletion & rotation
The backup system runs every day at midnight. When archives are done being created then the deletion process will begin. The deletion process is when NeQter removed old logs from visualized logs and archives. The age at which a log type is deleted is user configured. Archived logs and visualized logs have independent options on when they should be deleted. This means that a log can be within an archive and visualized at this same time.
Run time
The system automatically runs the backup service every day at 1 a.m. local time.
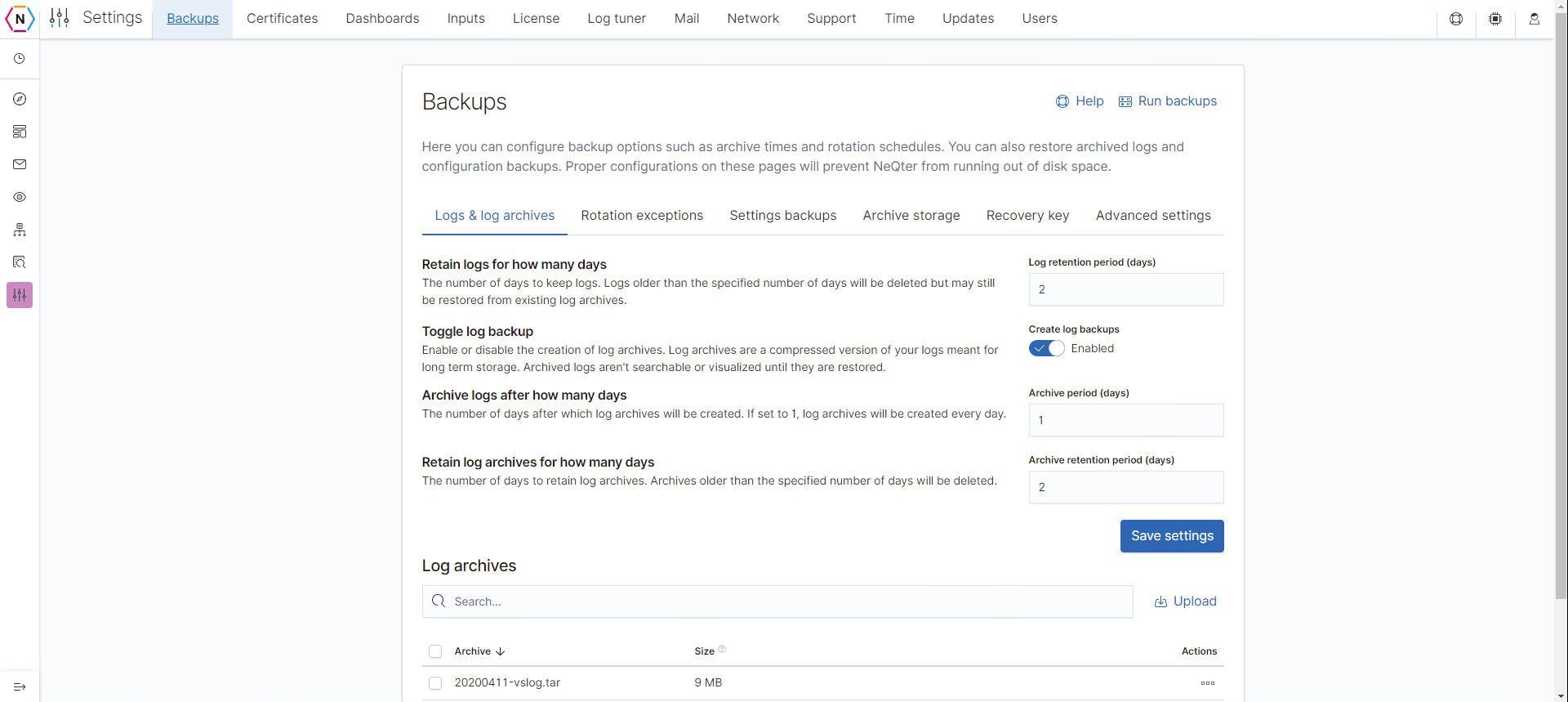
Configuration
There are four separate options that must be configured for logs.
- Retain logs after how many days: This determines when logs will be deleted from NeQter’s database. This means that the logs will no longer be searchable from the logs tab or displayed in dashboards.
- Toggle log backups: Enables or disables the creation of log archives. It is strongly suggested you leave this feature on to enable successful logging of your backups.
- Archive logs from NeQter after how many days: This represents the age at which a visualized log must be before it becomes archived. For example, if this number is set to 3 days then a log generated on Monday will be archived when the backup operating runs Thursday morning. As a note, this number must be less than when visualized logs are configured to be removed (the second and third configuration option on this tab).
- Retain log archives for how many days: This determines how long archived logs are to remain on the system before deletion. If a archived log is found to be on the system for longer than the set amount of days allocated then it is deleted. NIST compliance requires logs to be archived for at least 90 days.
NOTE: Once an archive is deleted there is no way to recover it!
Restore
When restoring indices from the log archives you have the ability to choose which indices you would like to restore from that day. You can choose multiple indices, or just one. Until the restore is finished you will not be able to save settings, delete archives, or restore from any other archives.
NOTE: This operation cannot be interrupted once it begins. This process may take a long time.
Rotation exceptions
A Rotation Exception is an index that you have manually chosen to not be automatically deleted due to age during the backup service process. It will only be deleted when it reaches its specified removal date.
Adding exceptions
To add an exception, go to Settings > Backups > Rotation Exceptions and then click the Add Index button to select one or more indexes to be exempt from the default retainment period. From here you will be prompted to select the date of which the log will be deleted.
NOTE: Removing exceptions does not remove the index, it only removes the exception from said index, allowing the default backup settings to take effect during the next run time.